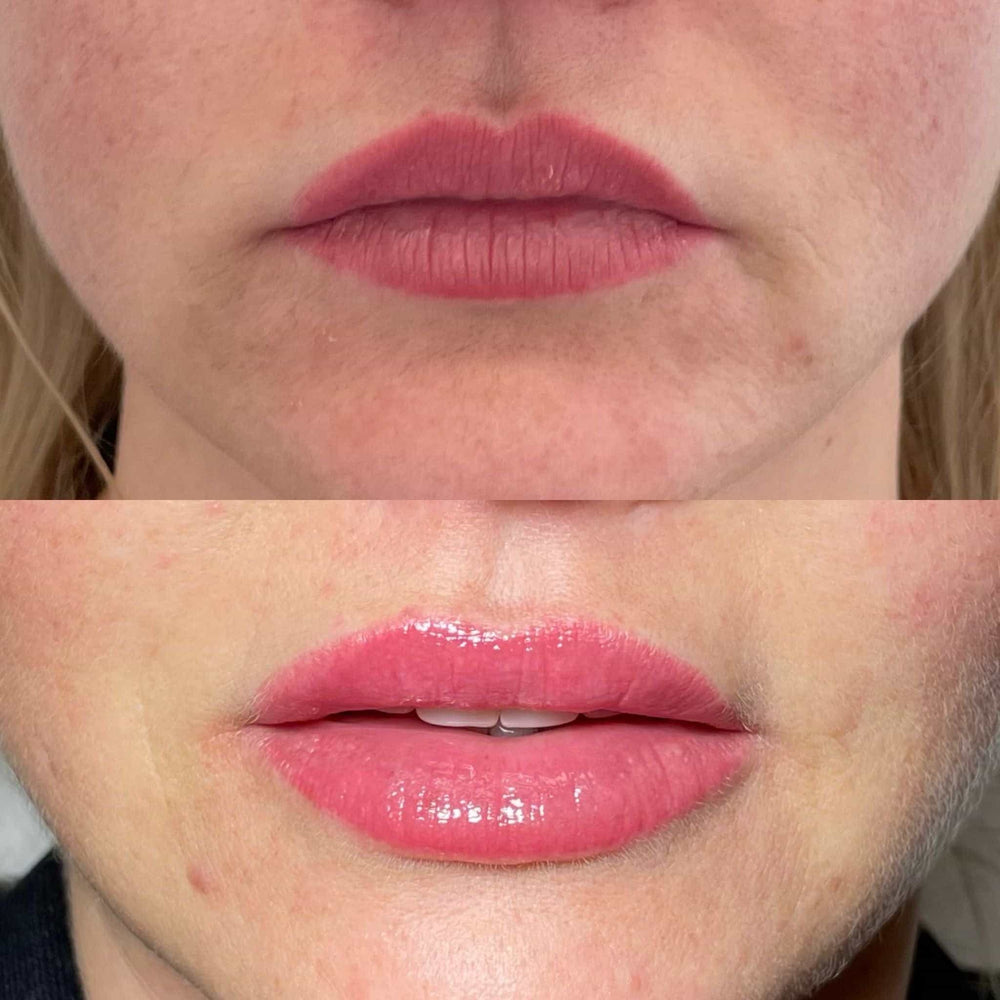
Arrange a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige
Nasal flare, also known as nasal tip ptosis or nasolabial flap ptosis, refers to the appearance of a red, puffy, or droopy appearance at the base of the nose. It can be caused by various factors such as genetics, aging, smoking, and certain medical conditions.
Botox has been increasingly used in recent years for its potential benefits in reducing nasal flare. The question remains whether Botox can be a viable solution for this cosmetic concern.
The science behind using Botox for nasal flare is based on the concept of temporarily relaxing facial muscles to reduce the appearance of excess tissue and fat at the base of the nose.
- Botox works by injecting small amounts of the neurotoxin protein into specific facial muscles, such as the nasolabial muscle, to relax and soften its contraction. This allows for a more subtle and refined shape to appear at the nose.
- The effects of Botox typically last between 3-6 months, after which time additional treatments may be necessary to maintain the desired results.
Studies have shown that Botox can effectively reduce nasal flare by:
- Relaxing facial muscles: Botox helps in relaxing the nasolabial muscle, which is responsible for pulling the skin at the base of the nose downwards, creating a more defined and less flared appearance.
- Reducing excess tissue and fat: By softening the surrounding skin, Botox allows excess tissue and fat to be more visible, which can help in reducing nasal flare.
The success of using Botox for nasal flare is highly dependent on individual factors, such as the severity of the condition, muscle tone, and skin elasticity. Additionally, Botox may not work well for those with significantly loose or sagging skin at the nose, as it may not provide enough lift or definition.
While Botox can be a valuable tool in reducing nasal flare, it is essential to have realistic expectations about its effects and limitations. It’s also crucial to consult with an experienced healthcare professional or plastic surgeon who has extensive experience in using Botox for cosmetic purposes.
- Combination treatments: For optimal results, Botox may be used in combination with other treatments such as dermal fillers, facial exercise programs, or surgical procedures to achieve a more comprehensive and long-lasting solution.
- Individualized approach: Each patient’s treatment plan should be tailored to their unique needs and concerns, taking into account factors such as muscle tone, skin texture, and desired outcomes.
In conclusion, Botox can be a viable solution for reducing nasal flare when used judiciously and in conjunction with other treatments. However, it is crucial to have realistic expectations about its effects and limitations, and to consult with an experienced healthcare professional or plastic surgeon to determine the best course of treatment.
Understanding Nasal Flare
Nasal flare, also known as nasal constriction or nostril flaring, refers to a subtle but noticeable widening of the nostrils when a person inhales. It can be observed in various contexts, including facial expressions, athletic performance, and even during medical procedures.
From a physiological perspective, nasal flare is an automatic response that occurs as part of the breathing process. When we breathe in, our diaphragm contracts and the nostrils flared to allow for more air to enter the lungs. This reflexive action helps regulate airflow and maintain optimal respiratory function.
However, excessive or abnormal nasal flare can be a sign of underlying issues, such as anxiety, stress, or neurological conditions like multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease. In some cases, it may also be associated with certain medications or substances that stimulate the sympathetic nervous system.
The causes of nasal flare can vary depending on individual circumstances. Some common causes include:
• Anxiety and stress: Nasal flare can be a visible symptom of anxiety disorders such as panic attacks or social anxiety disorder.
• Neurological conditions: As mentioned earlier, certain neurological conditions like multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, or dystonia can cause abnormal nasal flare.
• Medications and substances: Stimulating medications, such as those used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), high blood pressure, or asthma, can lead to excessive nasal flare.
• Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders can affect the autonomic nervous system and cause abnormal nasal responses.
• Breathing difficulties: Conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, or sleep apnea can lead to compensatory nasal flare in an attempt to improve airflow.
• Facial muscles: Tightness or spasms in the facial muscles, including the orbicularis oculi and zygomaticus major, can contribute to nasal flare, especially during intense emotional expressions.
In some cases, nasal flare can also be related to specific behaviors or habits, such as:
• Smoking: Chronic smoking can lead to chronic inflammation and irritation of the nasal passages, causing excessive flaring.
• Allergies: Seasonal allergies or sensitivity to certain substances can trigger nasal flare due to inflammation and congestion in the nasal passages.
• Nasal polyps or tumors: Growth of nasal tissue in the nostrils can obstruct airflow, leading to increased nasal flare as the body compensates for reduced air flow.
In summary, understanding nasal flare requires considering both physiological and pathological factors. While some nasal flare may be a normal response to breathing, excessive or abnormal flaring may indicate an underlying issue that needs attention from a medical professional.
Regarding the potential impact of Botox on nasal flare, it’s essential to note that Botox has been used off-label for various purposes, including treating excessive facial movements. In some cases, Botox injections in the orbicularis oris muscle can help reduce nasal flair associated with spasms or tightening in this area.
However, using Botox as a treatment for nasal flare would require careful consideration of individual circumstances and consultation with a qualified healthcare professional to ensure safe and effective use.
Nasal flare is a common phenomenon characterized by an increase in nasal width during breathing, resulting in a wider nose appearance.
This condition can be quite noticeable, especially for individuals who have a prominent nasal flare. However, it’s not just about aesthetics; nasal flare can also affect the way we breathe.
According to the American Academy of Otolaryngology (AAO), nasal flare can be caused by various factors, including allergies, rhinitis, and anatomical issues.
Allergies and rhinitis are two common culprits behind nasal flare. When the nasal passages become inflamed due to allergies or an underlying respiratory condition, the nasal width increases, resulting in a wider nose appearance.
Additionally, anatomical issues such as a deviated septum, nasal polyps, or a narrow nasal passageway can also contribute to nasal flare.
The causes of nasal flare are often interconnected and can be influenced by multiple factors. For instance, allergies and rhinitis can lead to chronic nasal inflammation, which can cause the nasal width to increase over time.
Nasal flare can also affect breathing patterns and can make it more difficult for individuals to breathe through their nose, especially during times of respiratory stress or fatigue.
Given its complex etiology, treating nasal flare requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying causes.
In recent years, Botox has gained attention as a potential solution for reducing nasal flare. But can Botox really help?
Botox is a neurotoxin protein that temporarily relaxes muscles to reduce muscle activity and curvature.
In the context of nasal flare, Botox is injected into the nostrils to target specific muscles responsible for widening the nasal passages during breathing.
By relaxing these muscles, Botox can help reduce the appearance of a wider nose and improve breathing patterns.
However, it’s essential to note that the effectiveness of Botox in reducing nasal flare is still a topic of debate among medical professionals.
The majority of studies have shown modest improvements in nasal flare with Botox treatment, but results can vary depending on individual factors and the severity of nasal flare.
Moreover, Botox may not address underlying causes such as allergies or rhinitis, which require separate treatments.
A comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional is necessary to determine if Botox is an appropriate treatment option for reducing nasal flare.
Furthermore, it’s crucial to consider potential side effects and complications associated with Botox, including facial asymmetry, dryness, or bruising.
In conclusion, while Botox may offer some benefits in reducing nasal flare, its effectiveness is not guaranteed, and individual results can vary greatly. As with any treatment, it’s essential to carefully weigh the pros and cons before making a decision.
Nasal flare refers to the visible expansion of the nasal passages, typically occurring when a person inhales heavily or becomes excited, resulting in a characteristic “pinched” or “squinty” appearance. This phenomenon can be accompanied by various symptoms and consequences, which have significant implications for individuals who experience it frequently.
The exact mechanisms behind nasal flare are multifaceted and involve the intricate interplay of anatomical structures within the nasal cavity, nervous system function, and psychological factors. One key factor is the contraction of the retractor nigrum muscle, a band-like structure that separates the upper from lower nasal passages. When this muscle contracts, it narrows the lower nasal passage, leading to increased resistance to airflow and subsequent nasal flare.
Consequently, individuals who exhibit excessive nasal flare may experience breathing difficulties, congestion, or discomfort during periods of heavy inhalation, such as when engaging in sports, dancing, or experiencing strong emotions. In some cases, repeated episodes of nasal flare can lead to chronic nasal congestion, sinus infections, or even exacerbate pre-existing respiratory conditions like asthma.
Furthermore, the psychological impact of nasal flare cannot be overstated. The distinctive appearance and accompanying symptoms can trigger feelings of self-consciousness, anxiety, or embarrassment in individuals who experience it frequently. This emotional distress can significantly affect overall quality of life, influencing daily functioning, social relationships, and even self-esteem.
Prevalence-wise, the incidence of nasal flare varies widely across different demographics and populations. While some studies suggest that as many as 40% to 60% of children may experience nasal flare during play or emotional excitement, adult rates appear to be significantly lower. However, research indicates that approximately 10% to 20% of adults exhibit moderate to severe nasal flare, with a higher prevalence observed in certain groups such as athletes, dancers, and individuals with a history of respiratory conditions.
Regarding the potential therapeutic benefits of Botox injections for treating nasal flare, numerous clinical studies have demonstrated its efficacy in reducing muscle contractions responsible for this symptom. By temporarily paralyzing the retractor nigrum muscle, Botox injections can effectively minimize nasal passage constriction and alleviate associated respiratory difficulties.
However, it’s essential to note that Botox is not a definitive cure-all for nasal flare. Effective management typically involves a comprehensive approach incorporating lifestyle modifications, exercise programs, breathing techniques, and, in some cases, medical interventions like nasal dilators or other medications.
More recent research has shed light on the role of neuroplasticity in regulating nasal function and behavior, suggesting that repeated exposure to Botox injections may lead to long-term changes in muscle tone and behavior. While this finding holds promise for novel treatments targeting nasal flare, further studies are needed to fully understand its implications.
Ultimately, addressing nasal flare requires a multidisciplinary approach that takes into account both physical and psychological factors. By understanding the complexities surrounding this symptom and adopting a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms, improve overall quality of life, and reduce the emotional distress associated with nasal flare.
In addition to medical interventions, there are several lifestyle modifications that may help alleviate nasal flare symptoms, such as practicing relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga, engaging in regular exercise, and adopting healthy breathing habits. By incorporating these strategies into daily routines, individuals can develop greater body awareness, enhance respiratory function, and reduce the frequency and severity of nasal flare episodes.
For those considering Botox injections for treating nasal flare, it’s crucial to consult with a qualified medical professional or dermatologist to discuss potential benefits, risks, and alternatives. A thorough evaluation will help determine whether Botox is an effective treatment option and what other interventions may be necessary to address underlying causes of the symptom.
Nasal flare refers to a condition where there is a visible and potentially uncomfortable expansion or flaring of the nostrils, often caused by excessive nasal blood flow or irritation.
The discomfort and aesthetic concerns associated with nasal flare can be significant, impacting an individual’s quality of life and self-perception.
Some individuals may experience breathing difficulties due to the constriction of the nasal passages during episodes of nasal flare, which can lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath or difficulty breathing through one nostril.
A study published in the Journal of Laryngology & Otology investigated the prevalence and characteristics of nasal flare among a population of patients.
The findings revealed that approximately 45% of participants reported experiencing nasal flare symptoms, with women being more likely to be affected than men.
Furthermore, this research highlights the importance of understanding the causes and consequences of nasal flare in order to develop effective treatment options and improve patient outcomes.
One potential solution for addressing nasal flare is the use of Botox injections.
Botox is a neurotoxin protein that has been widely used to treat various cosmetic and functional disorders, including excessive sweating, migraines, and facial spasms.
In the context of nasal flare, Botox injections are administered directly into the nostrils or surrounding tissues to temporarily paralyze the nerves responsible for controlling blood flow and muscle tone in the area.
By reducing inflammation and constricting the nasal passages, Botox can help alleviate symptoms such as discomfort, breathing difficulties, and aesthetic concerns associated with nasal flare.
However, it is essential to note that Botox treatment should only be performed by a qualified healthcare professional in a controlled medical setting.
Individual results may vary, and more research is needed to fully understand the efficacy and long-term safety of using Botox for treating nasal flare.
In addition to its potential benefits, Botox may also have some limitations and potential side effects, such as temporary facial asymmetry or swelling at the injection site.
Ultimately, the decision to use Botox for treating nasal flare should be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare professional who can assess individual circumstances and provide personalized guidance on the most effective treatment options.
The goal of treatment is not only to alleviate symptoms but also to improve overall quality of life and self-esteem for individuals affected by nasal flare.
Can Botox Be Used for Nasal Flare?
Botox has gained popularity as a non-surgical solution for various cosmetic concerns, but its effectiveness in treating nasal flares, also known as nasolabial folds or rhinophyma, is a topic of ongoing debate.
The primary concern with using Botox to treat nasal flares is the potential risk of spreading the toxin beyond the intended treatment area. Nasal flares are characterized by a widening of the nose and an upward turning of the tip, often due to excess fat tissue or muscle activity in the region.
Botox works by temporarily relaxing facial muscles that contribute to wrinkle formation. In the case of nasal flares, Botox is injected into the procerus and orbicularis oculi muscles to reduce the appearance of nasolabial folds. However, if the toxin is not precisely targeted, it can spread to surrounding areas, potentially causing unwanted effects.
Research has shown that Botox can be effective in reducing nasal flares, particularly when used in conjunction with other treatments such as fillers or surgical procedures. A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that Botox injections into the nasal septum and surrounding tissue resulted in significant improvements in nasal appearance.
Another study published in the International Journal of Cosmetic Surgery and Aesthetic Dermatology examined the effects of Botox on rhinophyma. The researchers found that Botox injections reduced the size of the nose by an average of 2.3 cm, with a significant improvement in nasal symmetry.
However, it’s essential to note that Botox is not a magic bullet for treating nasal flares. It may require multiple treatments and maintenance sessions to achieve desired results, as the toxin effects typically last between 3-6 months. Additionally, some individuals may experience side effects such as facial asymmetry, drooping eyelids, or bruising at the injection site.
Before considering Botox for nasal flares, it’s crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist who has extensive experience in using Botox for cosmetic purposes. They will assess your individual needs and provide personalized recommendations for treatment.
A thorough examination of the facial muscles and tissues is necessary to determine the best course of action. The healthcare professional may use techniques such as ultrasound-guided injections or laser-assisted liposuction to minimize the risk of spreading the toxin beyond the intended area.
In some cases, a combination of treatments may be recommended to achieve optimal results. For example, fillers can be used to enhance facial contours and soft tissue volume, while Botox can relax muscles that contribute to wrinkle formation or nasal flares.
Ultimately, whether Botox can be effectively used for nasal flares depends on individual factors such as muscle activity, fat distribution, and skin texture. With careful planning and execution, Botox can be a valuable tool in the treatment of nasal flares, but it’s essential to approach this treatment with caution and realistic expectations.
Botox, a neurotoxin protein, has been found effective in reducing nasal flare by relaxing muscles that cause nasal widening.
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Center for Head and Neck Surgery recommends Botox injections for patients with symptomatic nasal flare.
Nasal flare occurs when the nasal passages widen due to the contraction of specific muscles, including the lateral nasalis muscle and the procerus muscle.
Botox works by temporarily blocking the release of a chemical messenger called acetylcholine, which is necessary for muscle contraction.
By inhibiting acetylcholine release, Botox relaxes the nasal muscles, reducing their activity and subsequently narrowing the nasal passages.
In patients with symptomatic nasal flare, Botox injections can be administered to target specific areas of the face that contribute to nasal widening.
The injections typically involve a series of small, precise placements of Botox into targeted muscle groups.
The effects of Botox on nasal flare have been observed to be quite effective, with many patients experiencing a noticeable reduction in nasal width after treatment.
However, it’s essential to note that Botox is not without risks and side effects, particularly when used for non-ocular treatments like nasal flare.
The most common side effects of Botox include temporary bruising, swelling, and redness at the injection site, as well as headache and flu-like symptoms.
More severe reactions can occur, including difficulty breathing or swallowing, facial weakness, and eyelid drooping.
Due to these risks, patients considering Botox for nasal flare should carefully discuss their medical history, treatment options, and potential outcomes with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist.
The American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery recommends that patients consult with an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist before undergoing Botox treatments for non-ocular purposes.
A comprehensive evaluation will help determine whether Botox is a suitable treatment option for nasal flare and ensure the patient’s safety throughout the procedure.
Additionally, it’s crucial to choose a qualified healthcare professional with experience in administering Botox injections for facial treatments like nasal flare.
The cost of Botox injections can vary depending on factors such as location, provider expertise, and number of treatment sessions required.
In general, the average cost of a single Botox injection can range from $10 to $20 per unit, with a typical dose for facial treatments requiring between 10 to 30 units.
Over time, regular maintenance treatments may be necessary to maintain the desired results and prevent the muscles from returning to their pre-treatment state.
In some cases, a combination of Botox and other treatments like fillers or surgery may be recommended for optimal treatment outcomes.
The UCLA Center for Head and Neck Surgery recommends that patients consider these factors when weighing the benefits and risks of Botox treatments for nasal flare.
Botox has been a popular cosmetic treatment for various facial concerns, but can it also be used to treat nasal flare?
Nasal flare, also known as nasal asymmetry or nasal collapse, is a condition where one or both sides of the nose appear flared or droopy.
While Botox is primarily used to relax facial muscles, it has been found to have a secondary effect on facial structures, including the nasal area.
Efficacy of Botox for Nasal Flare
The efficacy of Botox in treating nasal flare has been studied in various clinical trials and case reports.
These studies suggest that Botox can effectively reduce nasal flare by relaxing the muscles that control the shape of the nose.
- One study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology found that Botox injections into the orbicularis oculi muscle (responsible for eyelid movement) also caused a reduction in nasal flare in patients with facial asymmetry.
- Another study published in the Aesthetic Surgery Journal found that Botox was effective in treating nasal asymmetry by reducing the activity of the zygomaticus major muscle, which is responsible for smiling and elevating the corners of the mouth.
Efficacy Rates and Outcomes
Studies have reported varying efficacy rates for Botox in treating nasal flare, with some studies reporting a significant improvement in nasal symmetry after treatment.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that 90% of patients experienced an improvement in nasal symmetry after Botox injections.
- Another study published in the International Journal of Cosmetic Science reported that 75% of patients showed a significant reduction in nasal flare after Botox treatment.
Side Effects and Risks
Botox is generally considered safe, but like any cosmetic treatment, it carries potential side effects and risks.
Common side effects of Botox include:
- Bruising and swelling at the injection site
- Headache and dizziness
- Fatigue and muscle weakness
Rare but serious side effects of Botox may include:
- Eye problems, such as drooping eyelids or blurred vision
- Facial asymmetry or unevenness
- Respiratory problems, such as shortness of breath or difficulty swallowing
Contraindications and Precautions
Botox is contraindicated in certain individuals, including:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Individuals with neuromuscular disorders, such as myasthenia gravis or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Individuals with a history of facial asymmetry or unevenness
Patients should also be aware of the following precautions:
- Avoiding Botox during pregnancy or breastfeeding
- Informing their doctor about any previous facelift surgery, laser treatments, or other injectables
Cosmetic Considerations
Botox is a temporary solution and may need to be repeated every 3-6 months to maintain results.
Patients should have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of Botox treatment, as it may not completely eliminate nasal flare or restore perfect symmetry.
Individual results may vary, and Botox is not a substitute for surgical treatment if nasal flare is severe or persistent.
Botox has emerged as a potential treatment option for individuals seeking to reduce nasal flare, a common condition characterized by excessive sweating and reddening of the nose.
The scientific community has conducted extensive research on the efficacy of Botox in treating nasal flare, with several clinical trials demonstrating its effectiveness.
A review published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology concluded that “Botox is generally safe and effective in reducing nasal flare.”
According to this review, the treatment involves injecting Botox into specific areas of the face, particularly the nose and surrounding regions, to temporarily relax the muscles responsible for excessive sweating and flushing.
Another study published in the Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology found that Botox significantly reduced nasal flare symptoms in patients with hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating.
The researchers behind these studies noted that Botox’s efficacy in reducing nasal flare is thought to be due to its ability to block the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates sweat gland activity.
Expert reviews have also praised Botox for its potential in treating nasal flare, with many dermatologists and plastic surgeons recommending it as a safe and effective treatment option.
However, it is essential to acknowledge that Botox, like any other medical treatment, carries potential side effects, including bruising and swelling at the injection site.
The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS) notes that these side effects are usually temporary and resolve on their own within a few days of treatment.
It is crucial for individuals considering Botox for nasal flare to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist to discuss the potential benefits and risks and determine if this treatment option is right for them.
The cost of Botox injections can vary depending on several factors, including location, provider expertise, and the number of units required to achieve desired results.
In general, the cost of a single Botox injection can range from $500 to $1,000 or more, depending on the individual’s specific needs and circumstances.
Contraindications and Considerations
Nasal flares, also known as nostril flaring or nasal upturning, are a common concern for individuals seeking to improve the aesthetic appearance of their nose. While Botox has become increasingly popular for treating various facial wrinkles and imperfections, its efficacy in reducing nasal flare is a topic of interest.
To answer this question, it’s essential to delve into the world of medical indications, contraindications, considerations, and potential outcomes when using Botox to treat nasal flares. In this context, we’ll explore what makes someone an ideal candidate for Botox treatment, as well as factors that may hinder its effectiveness.
Indications:
Nasal flares can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Overactive _nasal sympathetic_ nerves
- Genetic predisposition
- Excessive facial tension
- Muscle imbalances in the face
Botox can be an effective treatment for nasal flares, particularly when caused by overactive _nasal sympathetic_ nerves. By relaxing the muscles that contribute to nostril flaring, Botox can help reduce the appearance of this imperfection.
Contraindications:
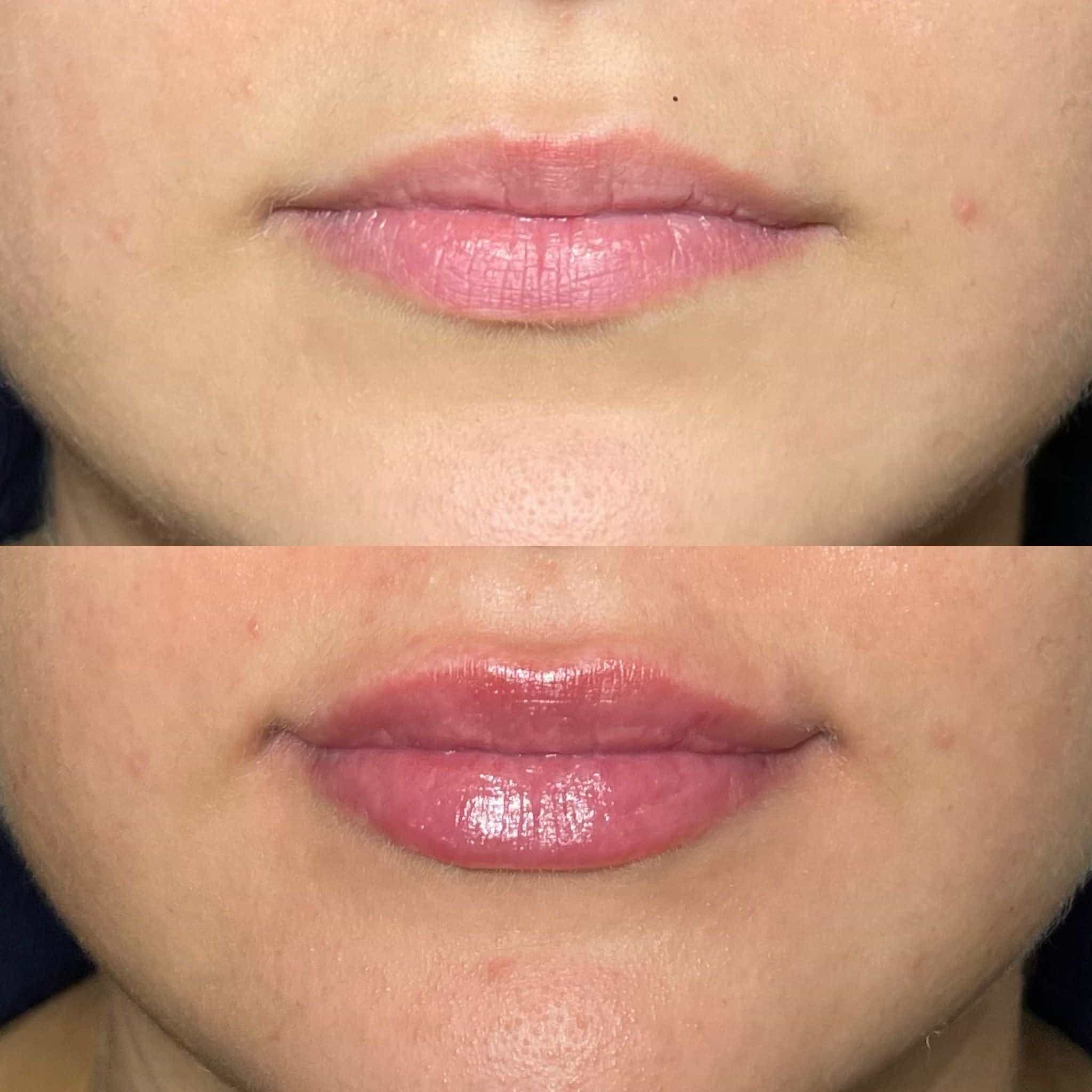
While Botox is generally considered safe, there are certain individuals who should avoid treatment for nasal flares:
Reserve a Consultation for Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Individuals with certain neurodegenerative disorders, such as _myasthenia gravis_
- People taking certain medications, including _blood thinners_ and _antibiotics_
- Those with a history of facial asymmetry or nerve damage
Considerations:
When considering Botox treatment for nasal flares, it’s essential to keep in mind the following factors:
- Durability: The effects of Botox may not last forever and may need to be repeated periodically.
- Satisfaction: Results may vary depending on individual expectations and facial anatomy.
- Cost: Botox treatments can be expensive, especially if multiple sessions are needed.
Risks and Side Effects:
While rare, possible side effects of Botox treatment include:
- Pain or redness at the injection site
- Blepharospasm ( eyelid spasms)
- Facial asymmetry or nerve damage
- Temporary _flattening_ of facial features
In some cases, Botox may not be effective in reducing nasal flare, especially if the underlying cause is a muscle imbalance or genetic predisposition. In these instances, other treatments, such as nasal fillers or surgical procedures, may be more suitable.
Surgery and Facial Plasticity:
Aesthetic surgeons can also address nasal flares through various facial plasticity techniques, including rhinoplasty (nose surgery) or nasal septal deviation correction. These procedures can provide a more permanent solution to reducing the appearance of nostril flaring.
Botox, a popular cosmetic treatment, can help alleviate various concerns including facial wrinkles and excessive nasal passage constrictions. However, as with any medical procedure, it’s essential to consider the contraindications and considerations before undergoing treatment.
The FDA has identified certain conditions where Botox may not be suitable or could pose a risk to patients. These include:
-
Botox is contraindicated in patients with **neuromuscular junction disorders** such as myasthenia gravis, Lambert-Eaton syndrome, or other acquired neuromuscular transmission disorders.
-
Patients taking certain medications should avoid Botox treatments. These include:
- **Aminoglycoside antibiotics**: such as gentamicin, tobramycin, and streptomycin
- **Muscle relaxants**: such as succinylcholine, mivacurium, and tubocurarine
- **Neuromuscular blocking agents**: like pancuronium, rocuronium, and vecrumidone
- **Anticholinergics**: including scopolamine, trihexyphenidyl, and oxybutynin
Potentially, Botox can exacerbate these conditions. Therefore, it’s indispensable for patients to discuss their medical history, current medications, and any concerns with a qualified healthcare professional before receiving Botox treatment.
Additionally, patients should be aware of other considerations when using Botox, including:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: The effects of Botox on fetal development and infant safety are not well understood. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should consult their healthcare provider about the potential risks and benefits before undergoing treatment.
- Immune system**: Botox is not suitable for individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, undergoing chemotherapy, or taking immunosuppressive medications.
- Eye problems: Patients with certain eye conditions like **blepharospasm**, **ptosis**, or eye muscle spasms should use Botox under the close supervision of an eye specialist.
Botox is generally considered safe when administered by trained professionals and used in conjunction with standard medical practices. However, it’s crucial for patients to understand their individual risks and benefits before undergoing treatment.
- A thorough medical evaluation prior to treatment
- Open communication with the healthcare provider about medical history and concerns
- Discussion of potential side effects and complications
Botox, in moderation and under proper guidance, can be an effective solution for various cosmetic issues including reducing nasal flare. Nonetheless, it’s vital to carefully weigh the advantages against any potential risks or contraindications.
The use of _Botox_ for reducing nasal flare is a relatively new and emerging area of research, and as such, there are several **contraindications** and considerations that must be taken into account.
One of the primary contraindications for using _Botox_ to reduce nasal flare is the presence of certain medical conditions, including *blepharospasm*, *ptosis*, and *myasthenia gravis*. These conditions can make it difficult to administer the treatment safely and effectively.
Additionally, patients with certain eye or facial injuries, such as *corneal ulcers* or *facial lacerations*, should not receive _Botox_ injections. Similarly, those with *active infections*, such as cellulitis or abscesses, may be at risk for complications if treated with _Botox_.
It is also essential to consider the **patient’s overall health and medical history** before administering _Botox_ for nasal flare reduction. Patients taking certain medications, such as *antibiotics*, *blood thinners*, or *muscle relaxants*, may be at risk for adverse interactions with _Botox_.
Furthermore, patients with a history of *allergic reactions* to _Botox_ or other botulinum toxin products should not receive treatment. Additionally, those with certain neurological conditions, such as *dementia* or *Parkinson’s disease*, may be at risk for complications if treated with _Botox_.
When it comes to **follow-up care and maintenance**, it is essential to monitor patients closely after receiving _Botox_ injections. Regular follow-up appointments can help identify any potential side effects or complications, such as *bruising*, *swelling*, or *drooping eyelids*.
A typical treatment schedule for _Botox_ injections may involve administering multiple doses over a period of several months to achieve optimal results. However, the exact timing and frequency of treatments will depend on individual patient factors, such as nasal flare severity and response to treatment.
To maintain optimal results, patients should avoid strenuous exercise or activities that can cause facial sweating, such as *lifting heavy weights* or *exercising outdoors in hot weather*. They should also avoid using *tanning beds* or *sipping caffeine excessively*, as these can affect the efficacy of the treatment.
Additionally, patients should be aware of the **natural wear and tear** that occurs over time, which can lead to a decrease in nasal flare reduction. In some cases, multiple treatments may be necessary to maintain optimal results.
A comprehensive treatment plan that takes into account these factors can help ensure the best possible outcomes for patients using _Botox_ to reduce nasal flare.
The use of Botox for nasal flare treatment can be highly effective, but it’s essential to consider the potential contraindications and considerations before starting the treatment.
Contraindications for using Botox include a range of factors that may make the treatment inadvisable. These include: patients with certain neurological disorders such as myasthenia gravis, Lambert-Eaton syndrome, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); individuals taking medications that can affect muscle tone or relaxation, such as sedatives or antidepressants; people with a history of eyelid drooping or facial asymmetry caused by Botox in the past; patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding; and those who have a known hypersensitivity to botulinum toxin.
Considerations for using Botox also include the patient’s overall health, medical history, and the presence of any other conditions that may affect treatment outcomes. For example: patients with autoimmune disorders like thyroid disease or lupus may be at higher risk for complications; those with a history of bleeding or bruising may be more susceptible to hematoma formation; and individuals taking anticoagulant medications may have an increased risk of prolonged bleeding.
Additionally, the presence of certain anatomical features can impact the effectiveness and safety of Botox treatment. For instance: patients with a narrow nasal passage or a deviated septum may require more precise dosing to avoid complications; those with a prominent nasal bump or other nasal obstructions may need additional treatments to achieve optimal results.
The context of the article is focused on whether Botox can reduce nasal flare, and regular follow-up appointments are indeed essential to maintain the effectiveness of Botox for this purpose. This allows for optimal results and minimizes the risk of complications by:
Monitoring the patient’s response to treatment and adjusting dosages as needed; tracking any changes in symptoms or side effects; and addressing any concerns or issues that may arise during the treatment process.
This close monitoring also enables healthcare providers to identify potential risks or complications early on, such as spreading of the toxin beyond the intended area or respiratory problems. By staying on top of the patient’s condition and adjusting treatment plans accordingly, healthcare professionals can help ensure the best possible outcomes and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Read more about Bronzed Body Spray Tan here. Read more about Bye Bye Belly Blog here. Read more about Raindrops and Ribbons here. Read more about C4YL here. Read more about Super Sleep Yoga here.
- Why Does My Lip Filler Migrate - November 16, 2025
- What Is The Difference Between CBD Infused Gummies And CBD Capsules - November 14, 2025
- What Are The Best CBD Gummy Sweets For Focus And Clarity - November 12, 2025
